-
 chevron_right
chevron_right
Texas sues Pfizer with COVID anti-vax argument that is pure stupid
news.movim.eu / ArsTechnica · Monday, 4 December - 23:13
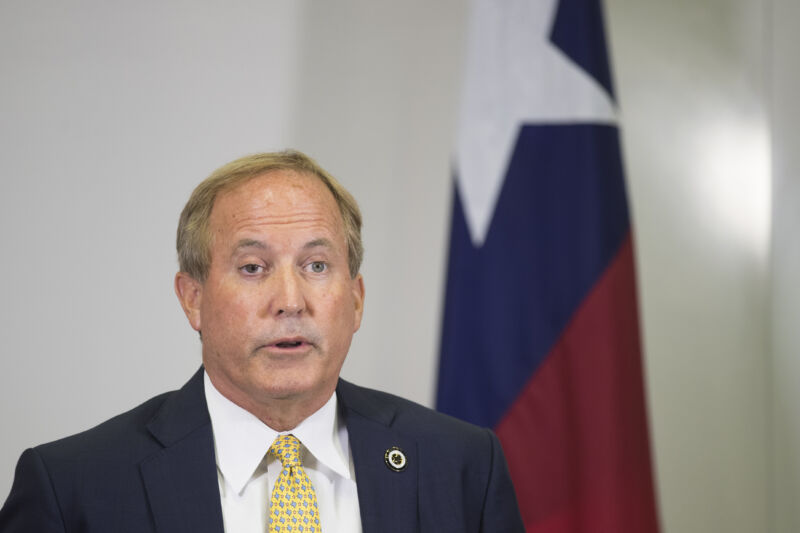

Enlarge / Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton. (credit: Getty | Brett Coomer/Houston Chronicle )
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton sued Pfizer last week, claiming the pharmaceutical giant "deceived the public" by "unlawfully misrepresenting" the effectiveness of its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and sought to silence critics.
The lawsuit also blames Pfizer for not ending the pandemic after the vaccine's release in December 2020. "Contrary to Pfizer’s public statements, however, the pandemic did not end; it got worse" in 2021, the complaint reads .
"We are pursuing justice for the people of Texas, many of whom were coerced by tyrannical vaccine mandates to take a defective product sold by lies," Paxton said in a press release. "The facts are clear. Pfizer did not tell the truth about their COVID-19 vaccines."