-
 chevron_right
chevron_right
Mars rover finds signs of seasonal floods
news.movim.eu / ArsTechnica · Wednesday, 9 August, 2023 - 19:34
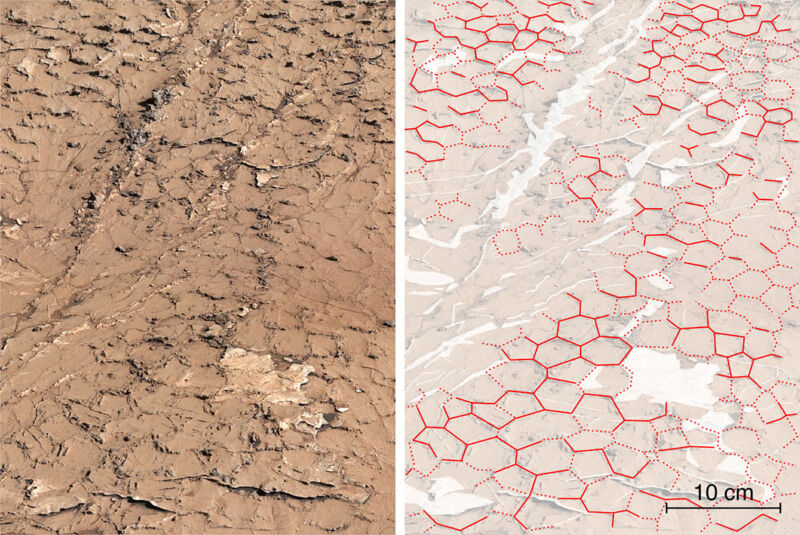

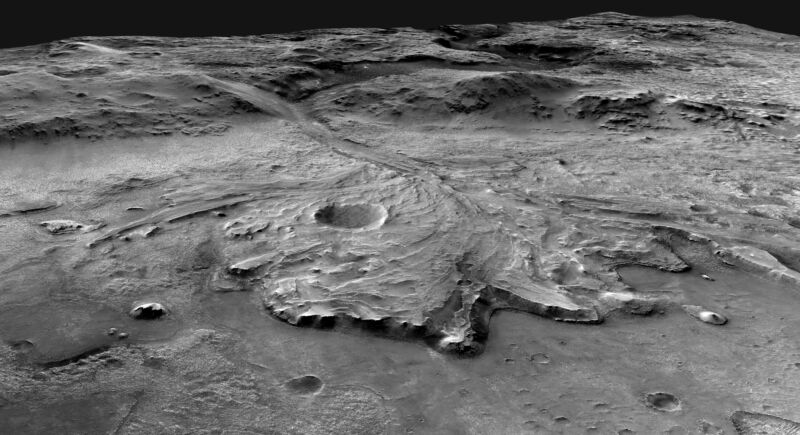
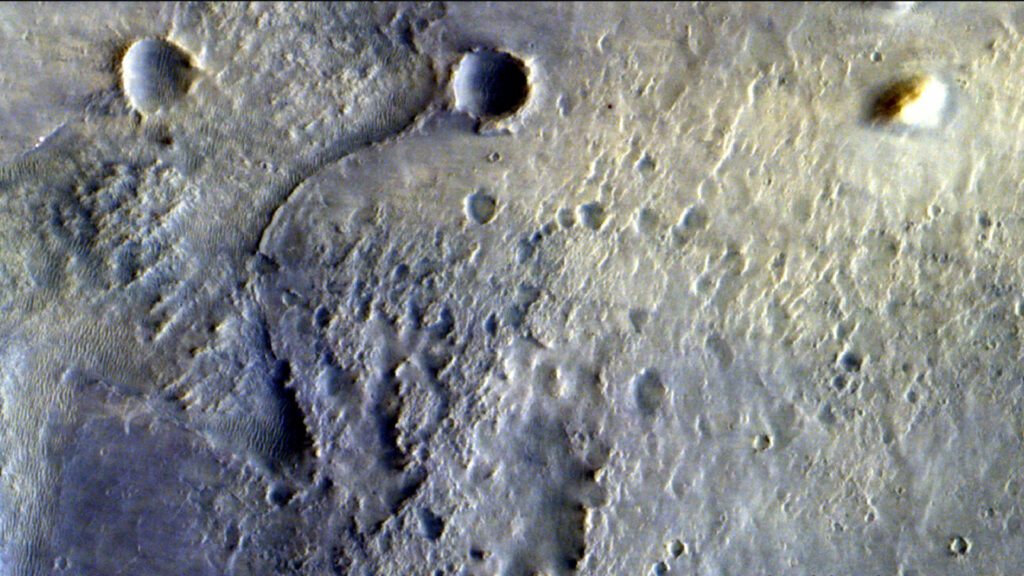
Enlarge / The newly described deposits (left) have their shapes highlighted in red at right. (credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/IRAP )
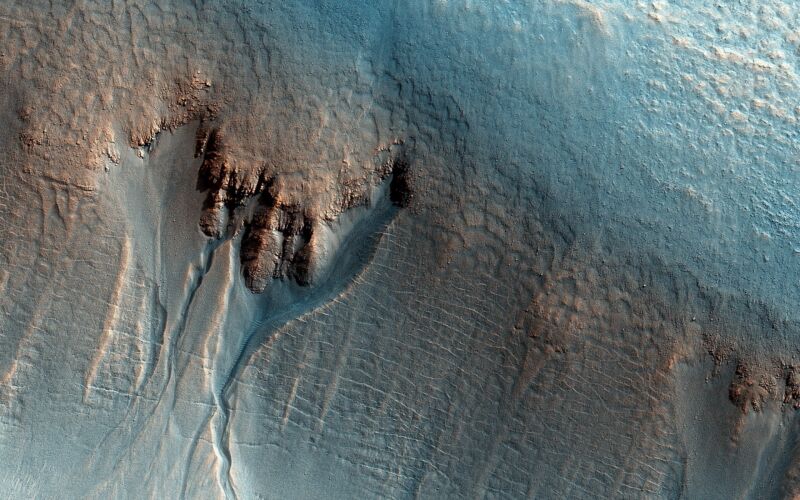
The prodigious evidence for water on Mars has eliminated scientific debate about whether Mars had a watery past. It clearly did. But it has left us with an awkward question: What exactly did that past look like? Some results argue that there were long-lived oceans and lakes on Mars. Others argue that the water largely consisted of ice-covered bodies that only allowed water to burst out onto the surface on occasions .
The picture is further confused by the fact that some or all of these may have been true at different times or in different locations. Creating a clear picture would help shape our understanding of an environment that might have been far more conducive to life than anything that exists on present-day Mars.
A new paper describes evidence that at least one part of Mars went through many wet/dry cycles, which may be critical for the natural production of molecules essential to life on Earth—though they don't necessarily mean conditions in which life itself could thrive.