-
 chevron_right
chevron_right
Here’s what we know about a mysterious launch from Florida this week
news.movim.eu / ArsTechnica · Tuesday, 5 September, 2023 - 22:32 · 1 minute
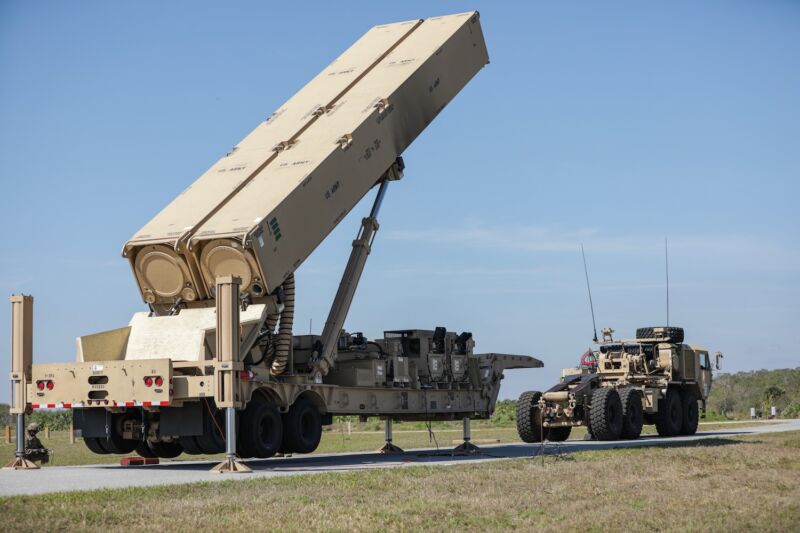

Enlarge / A US Army soldier lifts the hydraulic launching system on the new Long-Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW) during Operation Thunderbolt Strike at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida, on March 3. (credit: Spc. Chandler Coats, US Army )
Airspace and maritime navigation warnings released to pilots and mariners suggest the US military might launch a hypersonic missile this week on a test flight from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
This test could be one of the final milestones before the US Army fields the nation's first ground-based hypersonic weapon, which is more maneuverable and more difficult for an enemy to track and destroy than a conventional ballistic missile. Russia has used hypersonic in combat against Ukraine , and US defense officials have labeled China as the world's leader in emerging hypersonic missile technology.
That has left the US military playing catch-up, and the Army is on the cusp of having its first ground-based hypersonic missiles ready for active duty. If informed speculation is correct, the test launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station this week—performed in partnership between the Army and the Navy—could be a full-scale test of the new solid-fueled hypersonic missile to propel a hypersonic glide vehicle to high speeds over the Atlantic Ocean.